The GISCO statistical unit dataset represents the NUTS (nomenclature of territorial units for statistics) and statistical regions using multipart polygon, polyline and point topology. The NUTS geographical information is completed by attribute tables and a set of cartographic help lines to better visualise multipart polygonal regions.
The NUTS are a hierarchical system divided into 3 levels:
NUTS 1: major socio-economic regions
NUTS 2: basic regions for the application of regional policies
NUTS 3: small regions for specific diagnoses.
Also, there is a NUTS 0 level, which usually corresponds to the national boundaries.
Source
https://gisco-services.ec.europa.eu/distribution/v2/.
Copyright: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/gisco/geodata/administrative-units.
Arguments
- year
year character string or number. Release year of the file. See
giscoR::gisco_get_nuts()for valid values.- epsg
character string or number. Projection of the map: 4-digit EPSG code. One of:
"4258": ETRS89"4326": WGS84."3035": ETRS89 / ETRS-LAEA."3857": Pseudo-Mercator.
- cache
logical. Whether to do caching. Default is
TRUE. See Caching strategies section inesp_set_cache_dir().- update_cache
logical. Should the cached file be refreshed? Default is
FALSE. When set toTRUE, it will force a new download.- cache_dir
character string. A path to a cache directory. See Caching strategies section in
esp_set_cache_dir().- verbose
logical. If
TRUEdisplays informational messages.- resolution
character string or number. Resolution of the geospatial data. One of:
"60": 1:60 million."20": 1:20 million."10": 1:10 million."03": 1:3 million."01": 1:1 million.
- spatialtype
character string. Type of geometry to be returned. Options available are:
"RG": Regions -
MULTIPOLYGON/POLYGONobject."LB": Labels -
POINTobject.
- region
Optional. A vector of region names, NUTS or ISO codes (see
esp_dict_region_code()).- nuts_level
character string. NUTS level. One of
0,1,2,3orallfor all levels.- moveCAN
A logical
TRUE/FALSEor a vector of coordinatesc(lat, lon). It places the Canary Islands close to Spain's mainland. Initial position can be adjusted using the vector of coordinates. See Displacing the Canary Islands inesp_move_can().- ext
character. Extension of the file (default
"gpkg"). SeegiscoR::gisco_get_nuts().
Value
A sf object.
Details
The NUTS nomenclature is a hierarchical classification of statistical regions and subdivides the EU economic territory into regions of three different levels (NUTS 1, 2 and 3, moving respectively from larger to smaller territorial units). NUTS 1 is the most aggregated level. An additional Country level (NUTS 0) is also available for countries where the nation at statistical level does not coincide with the administrative boundaries.
The NUTS classification has been officially established through Commission Delegated Regulation 2019/1755. A non-official NUTS-like classification has been defined for the EFTA countries, candidate countries and potential candidates based on a bilateral agreement between Eurostat and the respective statistical agencies.
An introduction to the NUTS classification is available here: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/nuts/overview.
Note
Please check the download and usage provisions on gisco_attributions().
See also
giscoR::gisco_get_nuts(), esp_dict_region_code().
Other datasets representing political borders:
esp_get_capimun(),
esp_get_ccaa(),
esp_get_ccaa_siane(),
esp_get_comarca(),
esp_get_countries_siane(),
esp_get_gridmap,
esp_get_munic(),
esp_get_munic_siane(),
esp_get_prov(),
esp_get_prov_siane(),
esp_get_simpl,
esp_get_spain(),
esp_get_spain_siane(),
esp_siane_bulk_download()
Other nuts:
esp_get_spain()
Datasets provided by GISCO:
esp_get_ccaa(),
esp_get_munic(),
esp_get_prov(),
esp_get_spain()
Examples
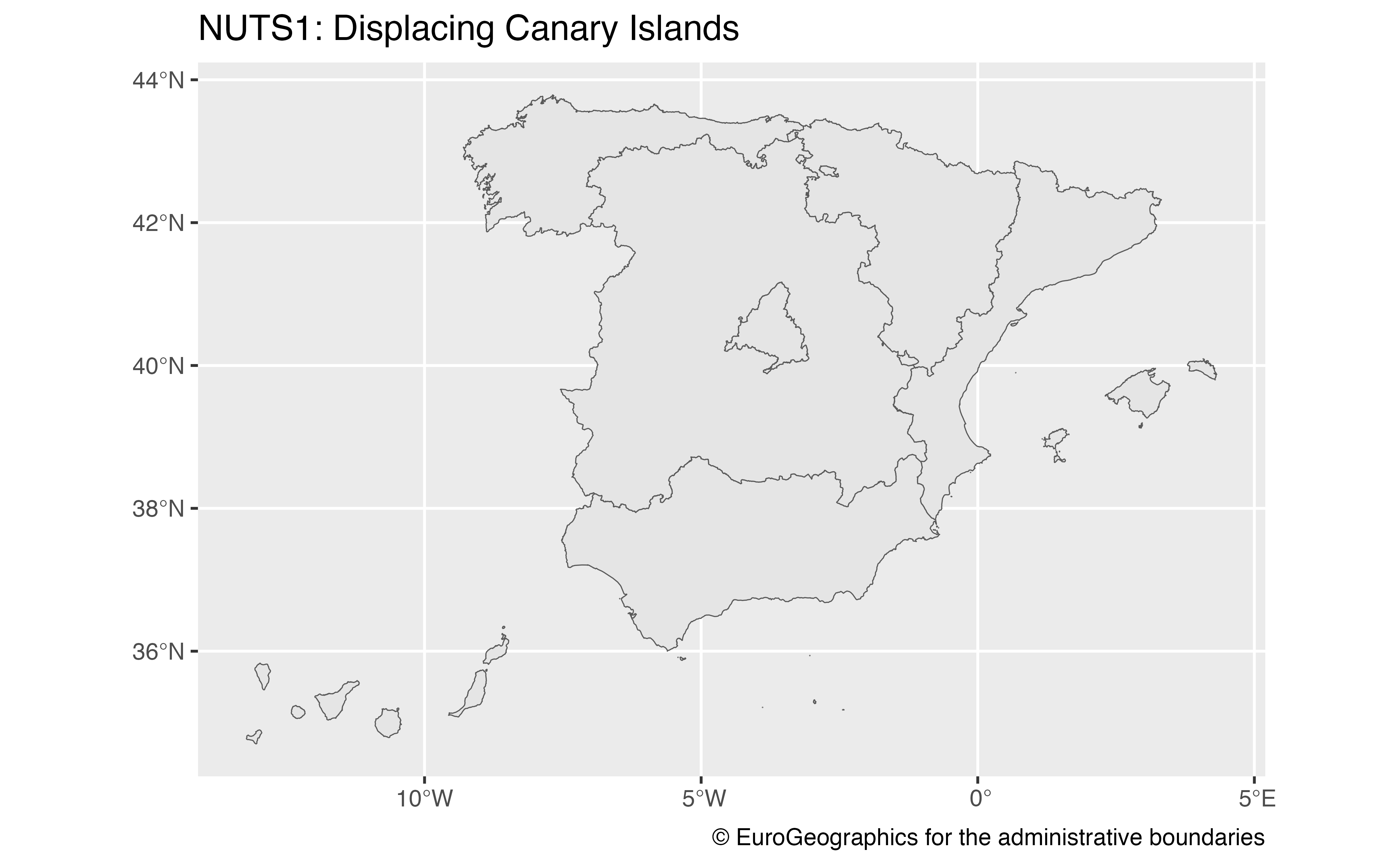
nuts1 <- esp_get_nuts(nuts_level = 1, moveCAN = TRUE)
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(nuts1) +
geom_sf() +
labs(
title = "NUTS1: Displacing Canary Islands",
caption = giscoR::gisco_attributions()
)
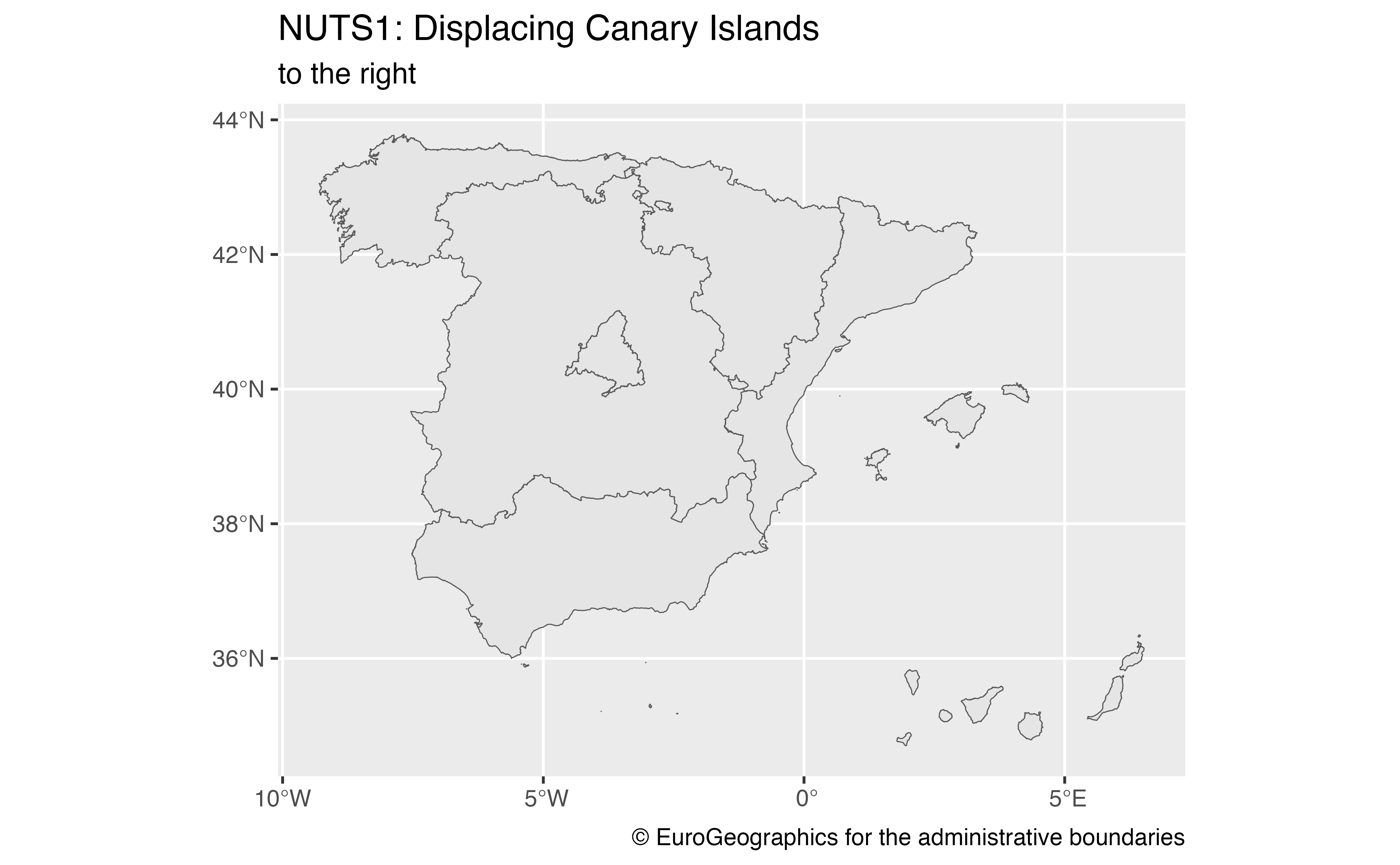
 nuts1_alt <- esp_get_nuts(nuts_level = 1, moveCAN = c(15, 0))
ggplot(nuts1_alt) +
geom_sf() +
labs(
title = "NUTS1: Displacing Canary Islands",
subtitle = "to the right",
caption = giscoR::gisco_attributions()
)
nuts1_alt <- esp_get_nuts(nuts_level = 1, moveCAN = c(15, 0))
ggplot(nuts1_alt) +
geom_sf() +
labs(
title = "NUTS1: Displacing Canary Islands",
subtitle = "to the right",
caption = giscoR::gisco_attributions()
)
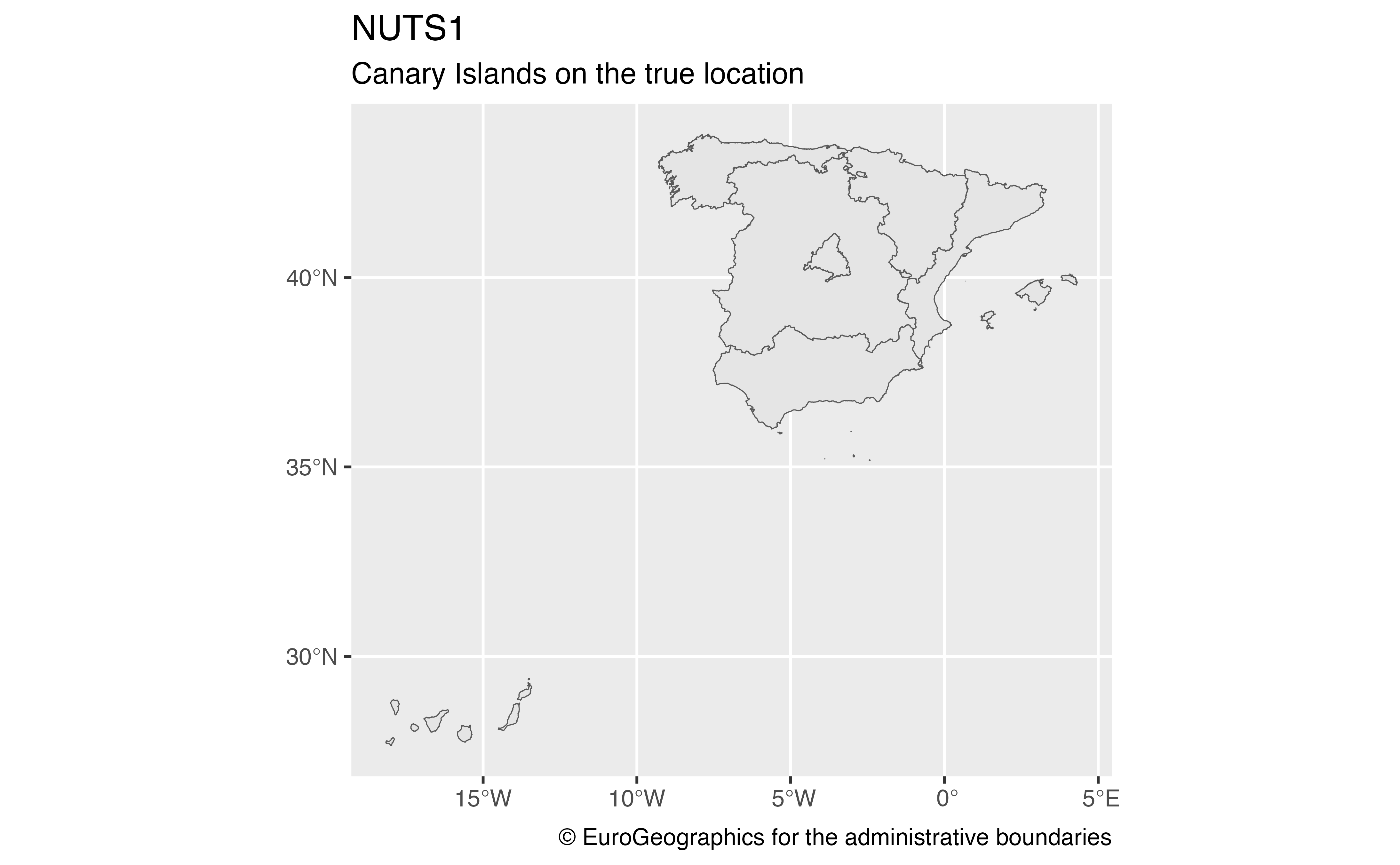
 nuts1_orig <- esp_get_nuts(nuts_level = 1, moveCAN = FALSE)
ggplot(nuts1_orig) +
geom_sf() +
labs(
title = "NUTS1",
subtitle = "Canary Islands on the true location",
caption = giscoR::gisco_attributions()
)
nuts1_orig <- esp_get_nuts(nuts_level = 1, moveCAN = FALSE)
ggplot(nuts1_orig) +
geom_sf() +
labs(
title = "NUTS1",
subtitle = "Canary Islands on the true location",
caption = giscoR::gisco_attributions()
)
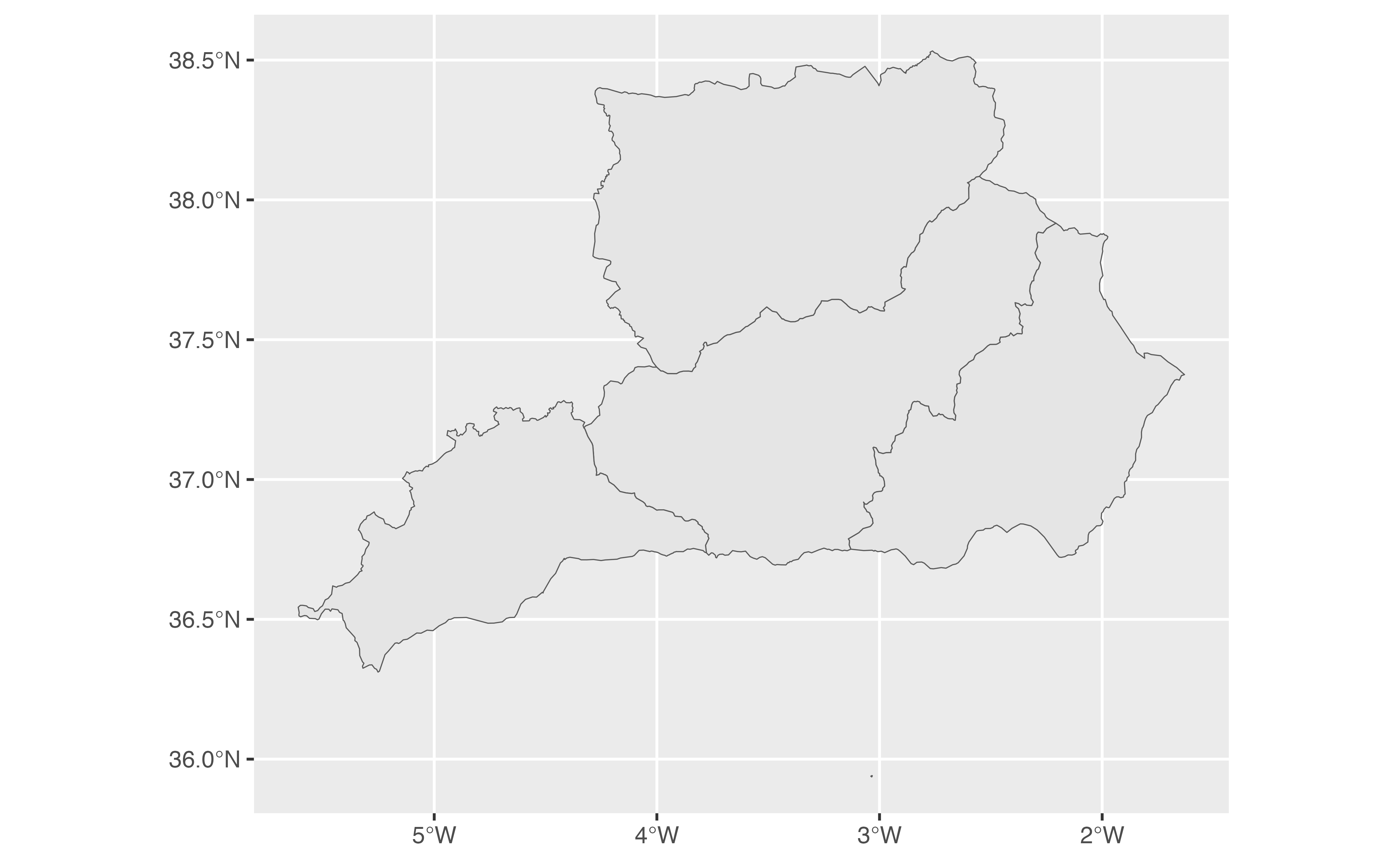
 and_orient <- esp_get_nuts(region = c(
"Almeria", "Granada",
"Jaen", "Malaga"
))
ggplot(and_orient) +
geom_sf()
and_orient <- esp_get_nuts(region = c(
"Almeria", "Granada",
"Jaen", "Malaga"
))
ggplot(and_orient) +
geom_sf()
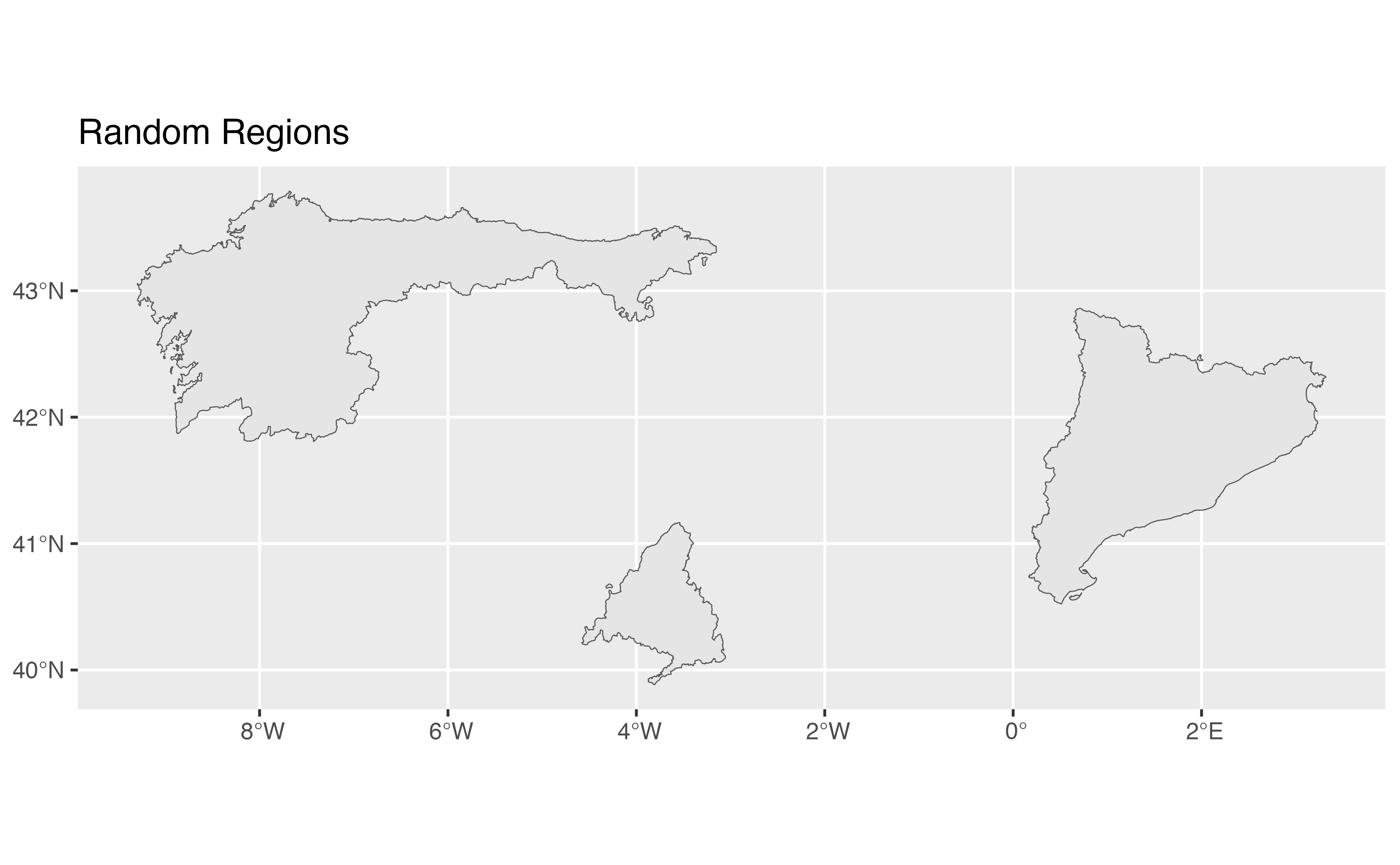
 random_regions <- esp_get_nuts(region = c("ES1", "ES300", "ES51"))
ggplot(random_regions) +
geom_sf() +
labs(title = "Random Regions")
random_regions <- esp_get_nuts(region = c("ES1", "ES300", "ES51"))
ggplot(random_regions) +
geom_sf() +
labs(title = "Random Regions")
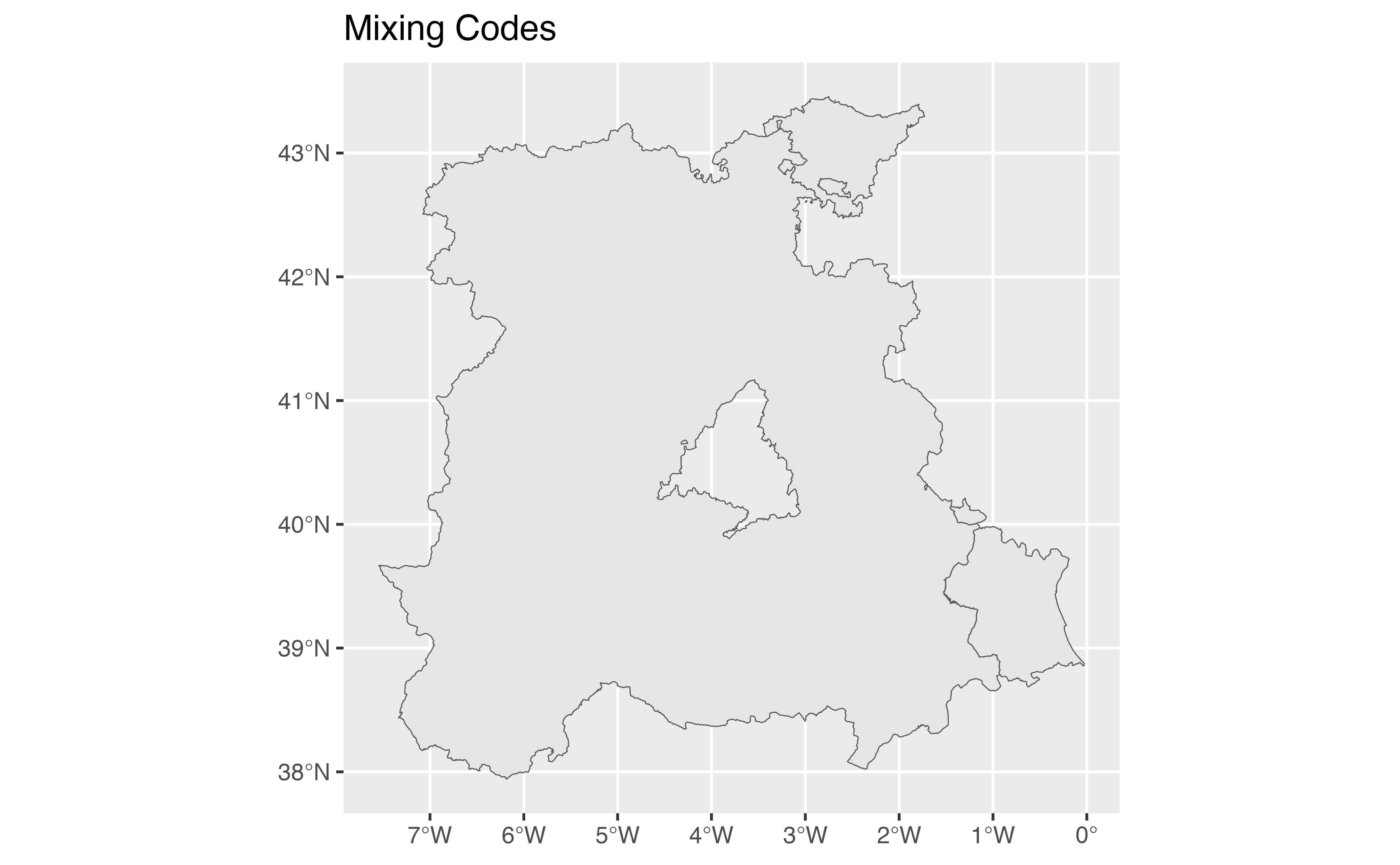
 mixing_codes <- esp_get_nuts(region = c("ES4", "ES-PV", "Valencia"))
ggplot(mixing_codes) +
geom_sf() +
labs(title = "Mixing Codes")
mixing_codes <- esp_get_nuts(region = c("ES4", "ES-PV", "Valencia"))
ggplot(mixing_codes) +
geom_sf() +
labs(title = "Mixing Codes")