Introduction
Full site with more examples and vignettes on https://ropenspain.github.io/mapSpain/
mapSpain is a package designed to provide geographical information of Spain at different levels.
mapSpain provides shapefiles of municipalities, provinces, autonomous communities, and NUTS levels of Spain. It also provides hexbin shapefiles and other complementary shapes, such as the demarcation lines around the Canary Islands.
mapSpain provides access to map tiles from Spain’s public institutions, which can be represented on static maps via mapSpain::esp_get_tiles() or on an R Leaflet map using mapSpain::addProviderEspTiles().
Additionally, mapSpain includes a powerful dictionary that translates province and region names to English, Spanish, Catalan, Basque, and Galician, and converts them to various coding standards such as NUTS, ISO2, and the INE (the official Spanish statistical agency) coding system.
Caching
mapSpain provides dataset and tile caching capabilities, which can be set as:
esp_set_cache_dir("./path/to/location")mapSpain relies on giscoR for downloading certain files, and both packages are well synchronized. Setting the same caching directory for both packages will speed up data loading in your session.
Basic example
Some examples of what mapSpain can do:
library(mapSpain)
library(ggplot2)
country <- esp_get_spain()
lines <- esp_get_can_box()
ggplot(country) +
geom_sf(fill = "cornsilk", color = "#887e6a") +
labs(title = "Map of Spain") +
theme(
panel.background = element_rect(fill = "#fffff3"),
panel.border = element_rect(
colour = "#887e6a",
fill = NA,
),
text = element_text(
family = "serif",
face = "bold"
)
)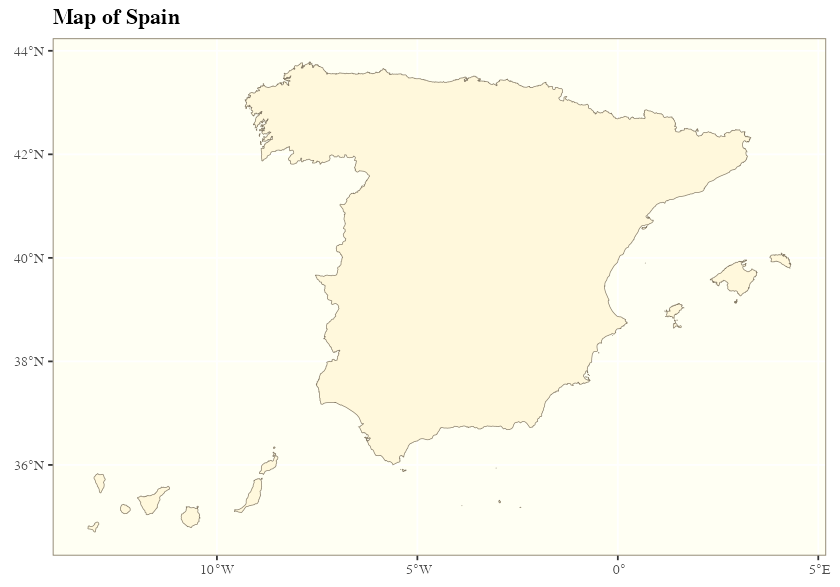
Example: Map of Spain
# Plot provinces
andalucia <- esp_get_prov("Andalucia")
ggplot(andalucia) +
geom_sf(fill = "darkgreen", color = "white") +
theme_bw()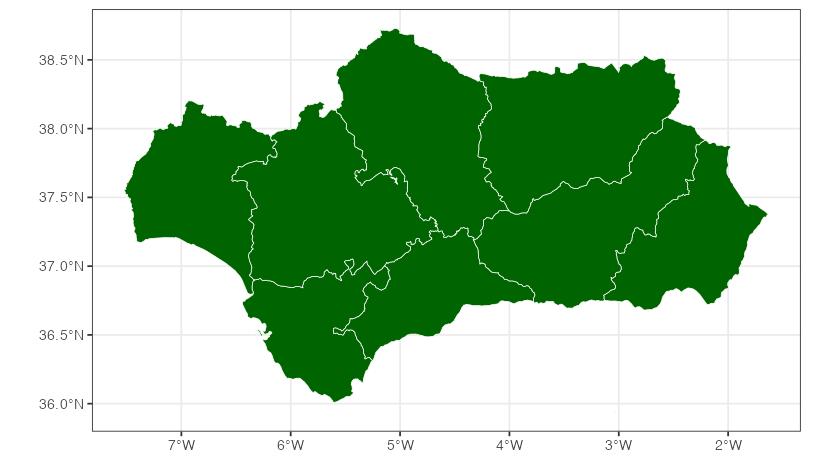
Example: Provinces of Andalucia
# Plot municipalities
euskadi_ccaa <- esp_get_ccaa("Euskadi")
euskadi <- esp_get_munic_siane(region = "Euskadi")
# Use dictionary
euskadi$name_eu <- esp_dict_translate(euskadi$ine.prov.name, lang = "eu")
ggplot(euskadi_ccaa) +
geom_sf(fill = "grey50") +
geom_sf(data = euskadi, aes(fill = name_eu)) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("red2", "darkgreen", "ivory2")) +
labs(
fill = "",
title = "Euskal Autonomia Erkidegoko",
subtitle = "Probintziak"
) +
theme_void() +
theme(
plot.title = element_text(face = "bold"),
plot.subtitle = element_text(face = "italic")
)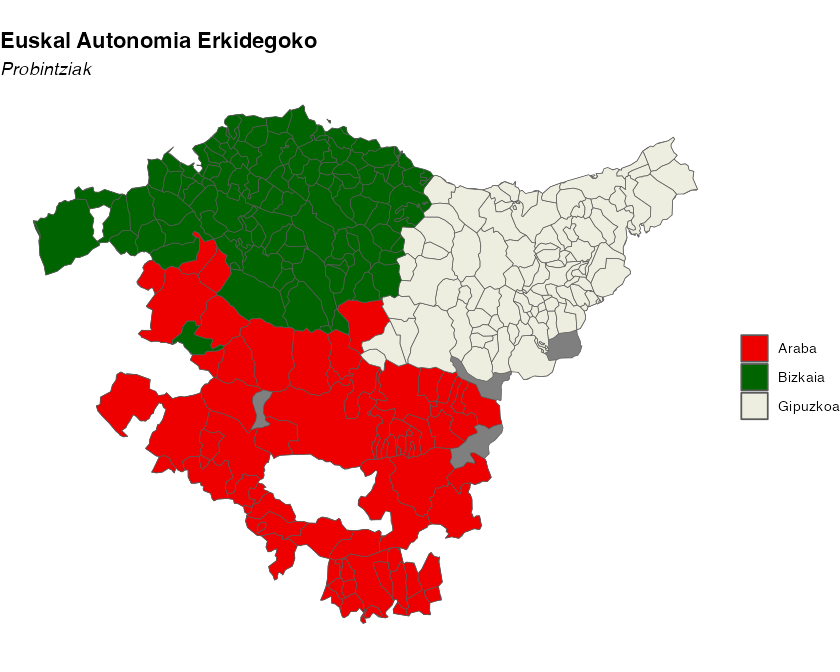
Example: Municipalities of the Basque Country
Choropleth and label maps
Let’s analyze the distribution of women in each autonomous community with ggplot2:
library(dplyr)
census <- mapSpain::pobmun25 |>
select(-name)
# Extract CCAA from base dataset
codelist <- mapSpain::esp_codelist |>
select(cpro, codauto) |>
distinct()
census_ccaa <- census |>
left_join(codelist) |>
# Summarize by CCAA
group_by(codauto) |>
summarise(pob25 = sum(pob25), men = sum(men), women = sum(women)) |>
mutate(
porc_women = women / pob25,
porc_women_lab = paste0(round(100 * porc_women, 2), "%")
)
# Merge into spatial data
ccaa_sf <- esp_get_ccaa() |>
left_join(census_ccaa)
can <- esp_get_can_box()
# Plot with ggplot
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(ccaa_sf) +
geom_sf(aes(fill = porc_women), color = "grey70", linewidth = .3) +
geom_sf(data = can, color = "grey70") +
geom_sf_label(
aes(label = porc_women_lab),
fill = "white",
alpha = 0.5,
size = 3,
linewidth = 0
) +
scale_fill_gradientn(
colors = hcl.colors(10, "Blues", rev = TRUE),
n.breaks = 10,
labels = scales::label_percent(),
guide = guide_legend(title = "% women", position = "inside")
) +
theme_void() +
theme(legend.position.inside = c(0.1, 0.6)) +
labs(caption = "Source: CartoBase ANE 2006-2024 CC-BY 4.0 ign.es, INE")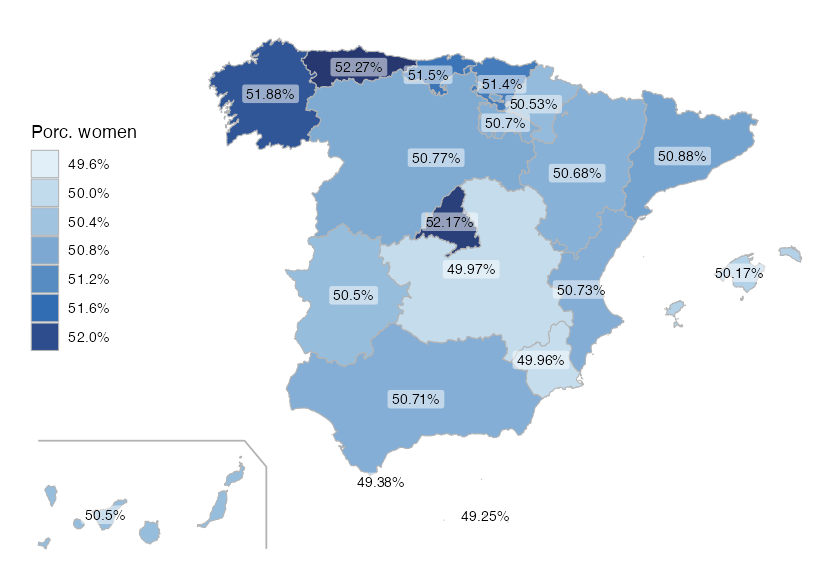
Percentage of women by Autonomous Community (2025)
Thematic maps
This example demonstrates how mapSpain can be used to create beautiful thematic maps. For plotting, we use the ggplot2 package, though any package that handles sf objects (e.g., tmap, mapsf, leaflet, etc.) could also be used.
# Population density of Spain
library(sf)
pop <- mapSpain::pobmun25 |>
select(-name)
munic <- esp_get_munic_siane(rawcols = TRUE) |>
# Get area in km2 from siane munic
# Already on the shapefile
mutate(area_km2 = st_area_sh * 10000)
munic_pop <- munic |>
left_join(pop) |>
mutate(dens = pob25 / area_km2)
br <- c(-Inf, 10, 25, 100, 200, 500, 1000, 5000, 10000, Inf)
munic_pop$cuts <- cut(munic_pop$dens, br)
ggplot(munic_pop) +
geom_sf(aes(fill = cuts), color = NA, linewidth = 0) +
scale_fill_manual(
values = c("grey5", hcl.colors(length(br) - 2, "Spectral")),
labels = prettyNum(c(0, br[-1]), big.mark = ","),
guide = guide_legend(
title = "Pop. per km2",
direction = "horizontal",
nrow = 1
)
) +
labs(title = "Population density in Spain (2025)") +
theme_void() +
theme(
plot.title = element_text(hjust = .5),
plot.background = element_rect(fill = "black"),
text = element_text(colour = "white"),
legend.position = "bottom",
legend.title.position = "top",
legend.text.position = "bottom",
legend.key.width = unit(30, "pt")
) +
labs(caption = "Source: CartoBase ANE 2006-2024 CC-BY 4.0 ign.es, INE")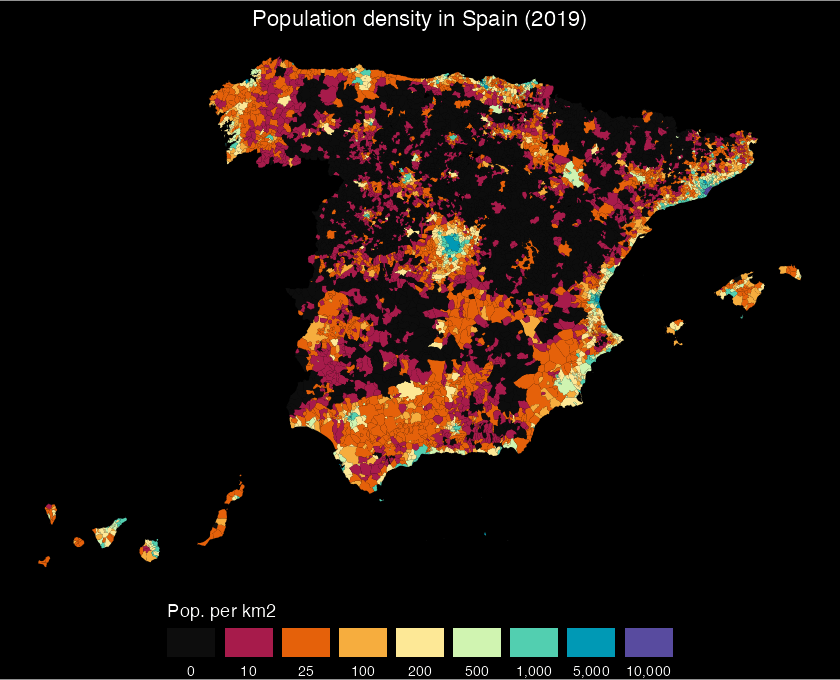
Population density in Spain (2025)
mapSpain and giscoR
If you need to plot Spain alongside other countries, consider using the giscoR package, which is installed as a dependency with mapSpain. Here’s a basic example:
library(giscoR)
# Set the same resolution for a perfect fit
res <- "20"
all_countries <- gisco_get_countries(resolution = res) |>
st_transform(3035)
eu_countries <- gisco_get_countries(
resolution = res,
region = "EU"
) |>
st_transform(3035)
ccaa <- esp_get_ccaa(
moveCAN = FALSE,
resolution = res
) |>
st_transform(3035)
# Plot
ggplot(all_countries) +
geom_sf(fill = "#DFDFDF", color = "#656565") +
geom_sf(data = eu_countries, fill = "#FDFBEA", color = "#656565") +
geom_sf(data = ccaa, fill = "#C12838", color = "grey80", linewidth = .1) +
# Center in Europe: EPSG 3035
coord_sf(
xlim = c(2377294, 7453440),
ylim = c(1313597, 5628510)
) +
theme(
panel.background = element_blank(),
panel.grid = element_line(
colour = "#DFDFDF",
linetype = "dotted"
)
) +
labs(caption = giscoR::gisco_attributions("es"))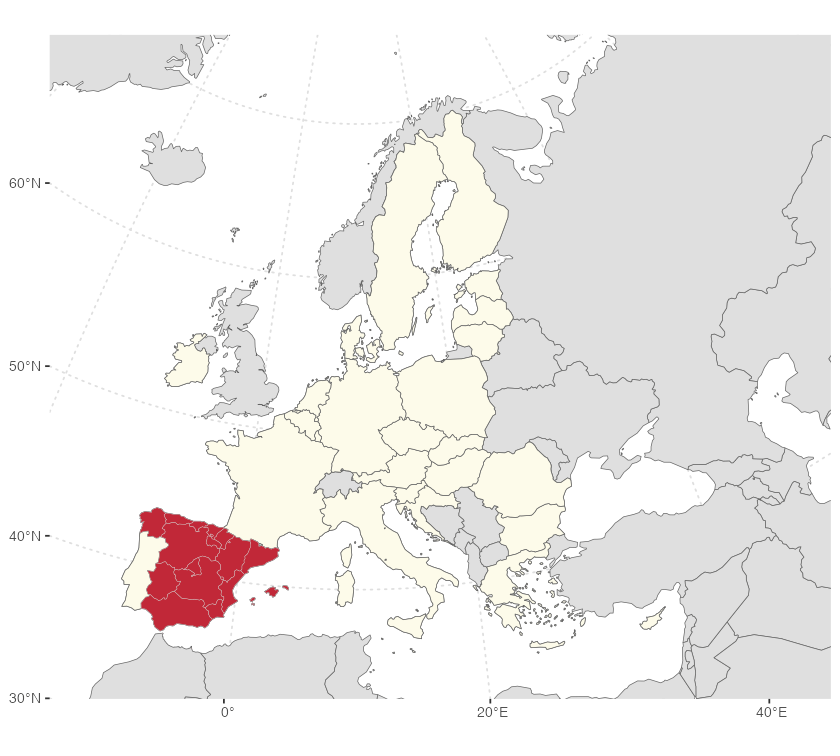
mapSpain and giscoR example
Working with tiles
mapSpain provides a powerful interface for working with imagery. It can download static files as .png or .jpeg files (depending on the Web Map Service) and use them alongside your shapefiles.
mapSpain also includes a plugin for the R Leaflet package, which allows you to include several basemaps on your interactive maps.
The services are implemented via the leaflet-providersESP Leaflet plugin. You can view each provider option at that link.
Note: When working with imagery, it is important to set moveCAN = FALSE in the esp_get_* functions. See Displacing the Canary Islands in help("esp_move_can", package = "mapSpain").